
Hip arthritis can make everyday activities difficult to perform. Things like walking, getting shoes and socks on and any activity that needs rotation of the hip can become difficult. It can even become difficult to get a restful night of sleep. If non-surgical treatments aren’t effective, surgery may be your best option to relieve hip pain and stiffness.
What is Robot Assisted Hip Replacement?
During hip replacement, the damaged bone and cartilage of the hip is removed, and replaced with metal, plastic and ceramic implants. These components reconstruct ball and socket of the hip joint. To make space for the metal implants, the bone of the socket (acetabulum) and the thighbone (femur) need to be prepared carefully. Using the Stryker Mako robotic-arm during hip replacement allows us to pre-plan your surgery on a 3D model, more precisely remove bone and cartilage and place hip replacement implants in the ideal position to improve range of motion and reduce wear on the implants.
Why is it used?
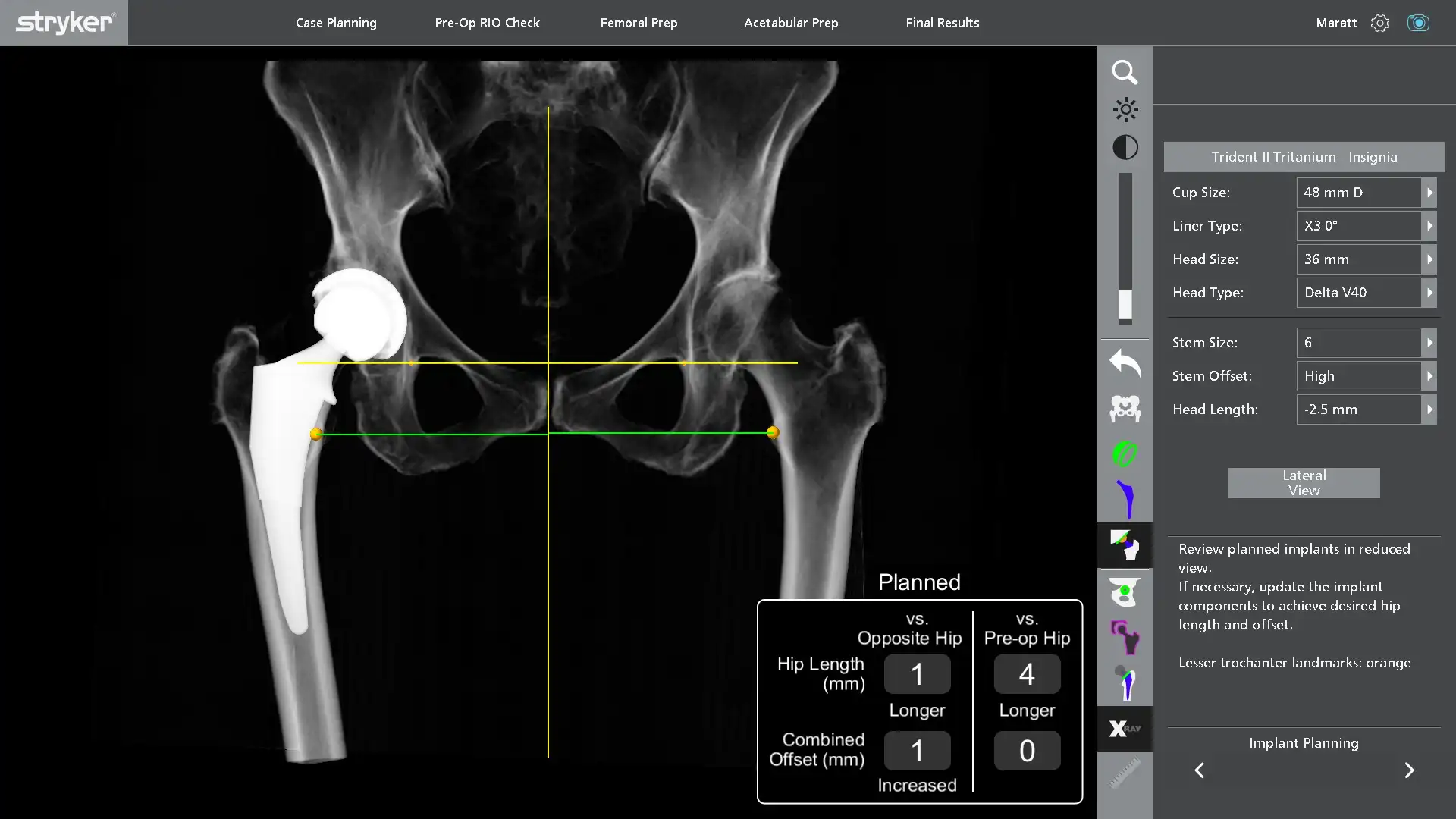
The preparation of bone and position of the implants in hip replacement is really important. Well positioned implants result in a hip replacement that feels better, has a more natural range of motion and is easier to recover from. Ideally positioned implants also reduce the risk of hip dislocation and early implant wear. During a robot assisted hip replacement, we can plan the implants that will be used on a 3D model allowing us to preserve as much bone as possible and be more precise in the reconstruction plan than with 2D X-rays. The robotic arm helps prepare the bone and also helps place the metal socket in the ideal position that we selected on the 3D model.
How does it work?
It starts a few weeks before your surgery date with a CT scan of your leg. Using the information from this CT scan, a 3D model of the pelvis and hip is made on which we can see the shape of the bones and bone spurs that need to be removed during the surgery. On this model, we can precisely select the position of the hip replacement implants to reconstruct the hip joint and make up for worn cartilage and bone.
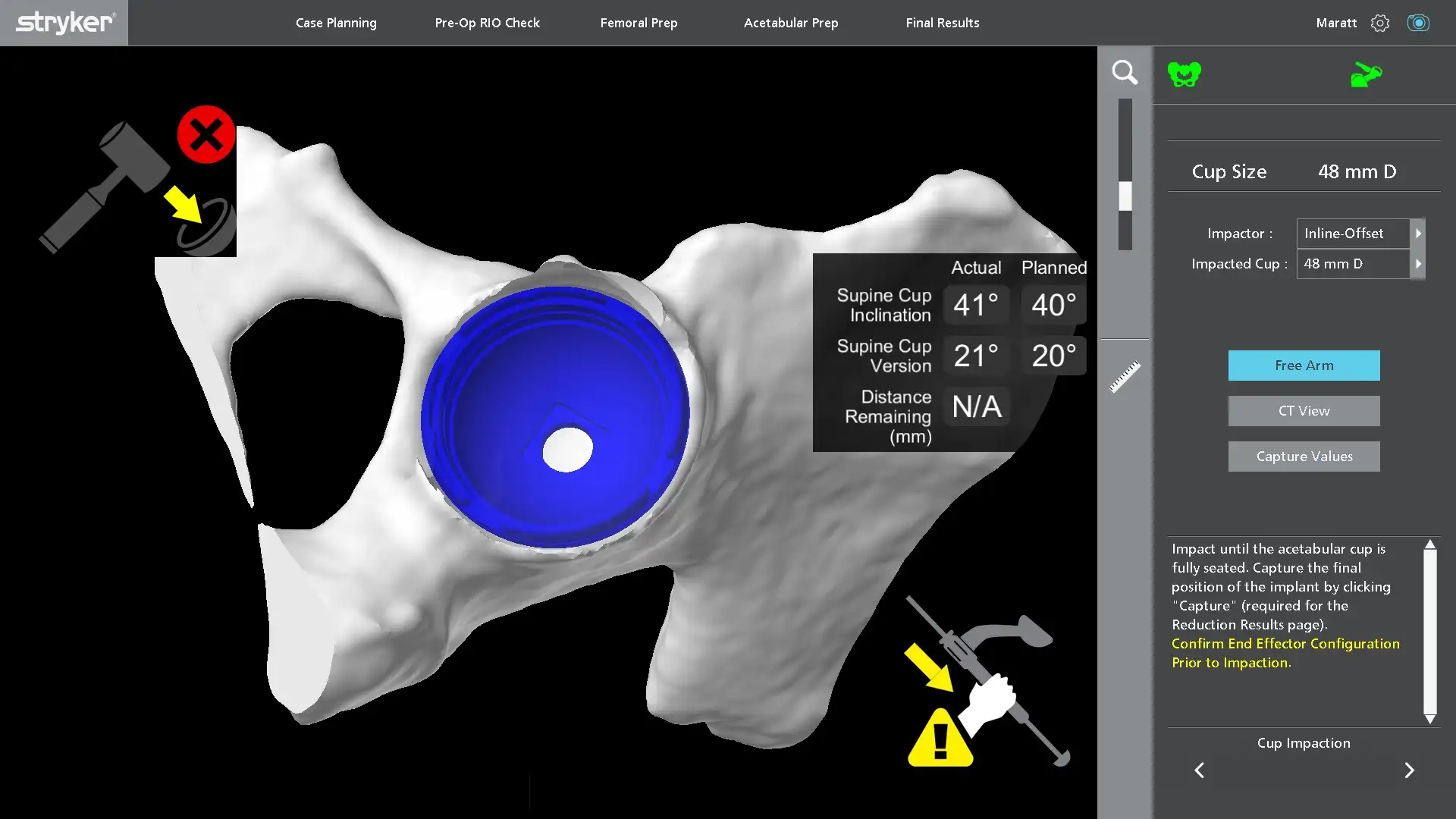
On the day of surgery, the navigation camera is shown a set of points on the bones of hip joint which it matches to the 3D model. At that point, the robotic system knows where the pelvis and femur are and can measure changes in the position of the joint. When the surgeon is using the robotic arm to prepare the socket, the software sets up a safe boundary to remove only the necessary amount of bone around the hip to add an extra layer of safety. Once the femur is prepared, trial implants are placed to make sure the reconstructed hip matches up with the plan on the software before placing the real implants.
