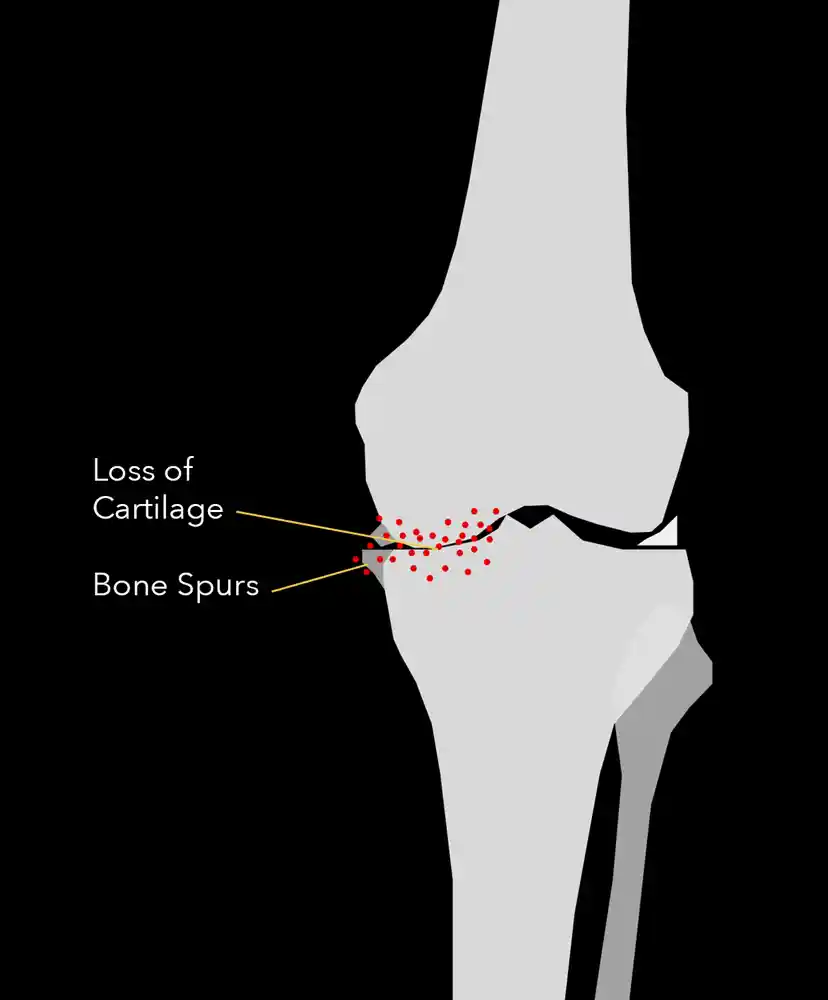
Arthritis is a degenerative disease that results in loss of cartilage, or cushion surrounding the ends of the bones. This condition is usually from overuse, or wear and tear over time. Also known as osteoarthritis (OA), or degenerative joint disease.
Symptoms of Knee Arthritis
Pain: When the cartilage surrounding the bones in the knee joint breakdown, the bones become closer together. This loss of space (cartilage) can cause increased pain as the knee bones articulate with one another, particularly with weight bearing activities or movement of the knee joint. Pain may be felt diffusely throughout the knee, or may be localized to a specific area depending where the arthritis is located.
Decreased mobility: Pain is typically increased with weight bearing activities such as rising from a chair, or walking. The motion of the knee joint may also be limited due to pain.
Additional symptoms include swelling, cracking or crepitus of the knee with movement, and stiffness of the knee joint, particularly in the morning. Depending on the location of the arthritis, you may develop a knee deformity or change in alignment of the knee. This may result in a bowing appearance (varus alignment) or knock-kneed appearance (valgus alignment).
Diagnosis
An x-ray is typically used to diagnose osteoarthritis of the knee. The x-ray will show narrowing of the joint space between the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shinbone). It may also show bone spurs and other signs of degeneration.
A physical examination from an orthopedic specialist or primary care provider can also aid in the diagnosis of arthritis. Examination may demonstrate limited range of motion, swelling, and pain along the joint line.
Treatment Options
Non-surgical
It is recommended that you initially treat knee pain caused by arthritis with non-operative interventions. Here are some of the non-operative treatments options:
- Activity modification
- Weight loss through diet and exercise
- Use of an assistive device (i.e cane, walker) to off-load the lower extremity
- Physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding knee musculature, particularly the quadriceps muscle
- Medications such as Tylenol or NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatories)
- Knee injection (cortisone or visco-supplementation)
Surgical
If non-operative options are no longer beneficial, surgical intervention may be an option to treat knee pain causes by arthritis. Surgery is typically reserved for severe loss of cartilage and arthritis associated with progressive pain.
Knee Pain Knee Replacement